notes prepared by subhankar Karmakar
1. CELLS:
A cell is the smallest unit of life which has a definite structure and performs a specific function.
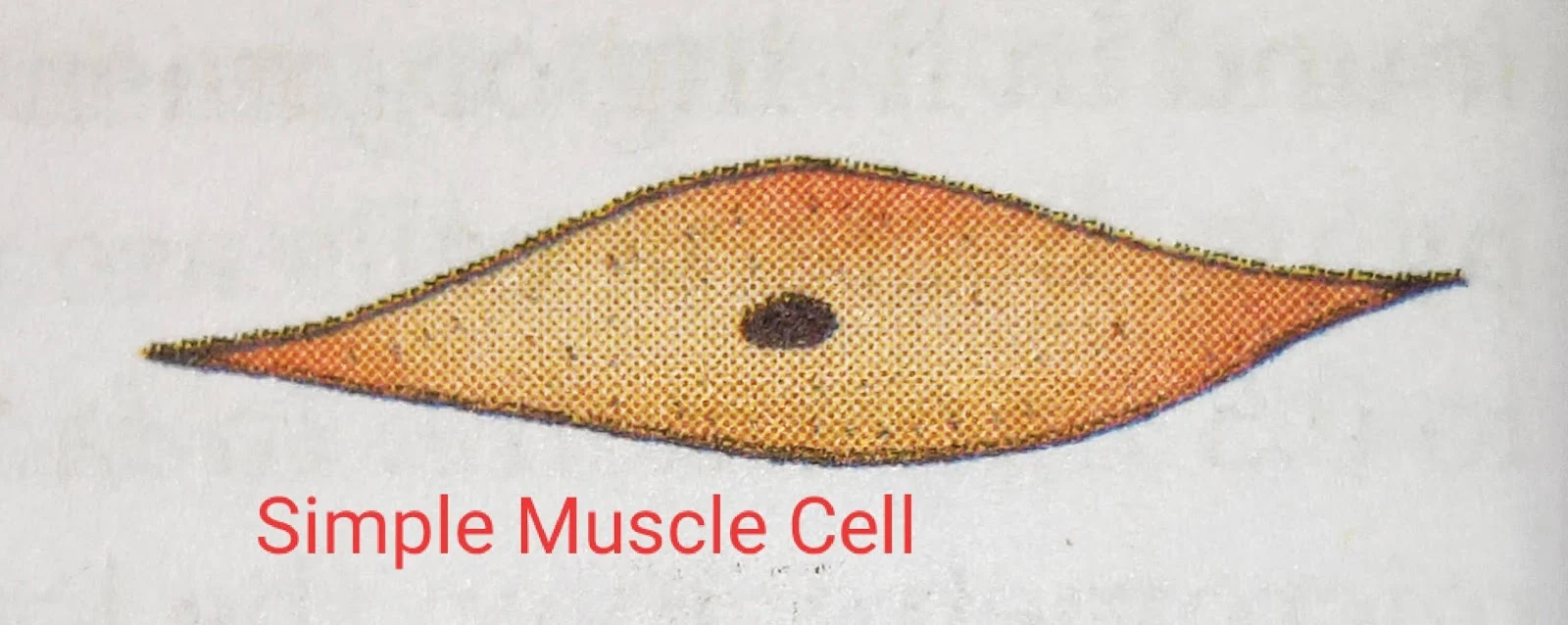
All the cells of a multicellular organism are not similar. They are of many different shapes and sizes. Most of the cells are specialised to perform particular functions. They are called specialised cells. For example, in animals, muscle cells are specialised to contract and relax so that they can bring about movement in body parts. In plants, photosynthetic cells are specialised to carry out photosynthesis and make food. There are many types of specialised cells in animals and plants which perform different functions.
2. TISSUES:
The group of similar cells which work together to perform a particular function is called a tissue. For example, in animals, muscle tissue specialised to contract and relax so as to move body parts. Therefore, muscle tissue brings about movement in the body parts of animals. In plants, photosynthetic tissue is a group of photosynthetic cells joined together which is specialised to do photosynthesis and make food. There are many different types of tissues in both, animals as well as in plants.
3. ORGANS:
An organ is a collection of different tissues which work together to perform a particular function in the body of an organism.
The multicellular organisms are made up of different organs which do different jobs for the organism. Some of the organs in animals are:
Heart, Stomach, Brain, Lungs, Kidney, etc.
Some of the organs in plants are:
Roots, Stem, Leaf, Flower etc.
Each organ does different specialised work.
Like in animals,
a. The function of heart is to pump blood around the body.
b. The function of brain is to control all the parts of the body.
c. The function of lungs is to take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
d. The function of the stomach is to digest the food.
In plants,
a. The function of the roots is to absorb water and dissolve mineral salts from the soil.
b. The function of stem is to carry water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and the prepared food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
c. The function of a leaf is to prepare food for the plant by the process of photosynthesis.
d. The flowers are reproductive organs which led to the formation of fruits and seeds. The fruit protects the seeds.
4. ORGAN SYSTEMS:
A group of interconnected organs which works together to do a big job for the organism, is called an organ system.
All the multicellular animals and plants have many organ systems in their bodies to carry out various life processes.
For example, the various organ systems of animals are:
Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, nervous system, excretory system, reproductive system, muscular system and skeletal system.
The plants have two main organ systems:
Root system and shoot system.
Work of the organ systems:
The function of digestive system is to break down the food into simple substances which can be absorbed by the body. The main organs of the digestive system are:
Mouth, Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
5. ORGANISM:
An organism is an animal or a plant which can exist on its own. An organism is made up of many different organ systems which work together to perform all the functions necessary for maintaining life.
Multicellular organisms are built like in the following sequence.
1. Cells make up tissues
2. Tissues make up organs
3. Organs make up organ systems
4. Organ systems makeup an organism




No comments:
Post a Comment