notes prepared by subhankar Karmakar
Numericals on concave mirror:
Q1. What is the nature of a mirror having a focal length of, + 4 cm?
1. Ans. As the focal length is positive, the mirror is convex mirror.
Q2. What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, - 6 cm?
2. Ans. As the focal length is negative, the mirror is a concave mirror.
Q3. If the radius of curvature of a mirror is - 20 cm, what will be its focal length? What type of mirror it is?
3. Ans. As the focal length is half of the the radius of curvature, so, f = -10 cm. As the focal length is negative it is a concave mirror.
Q4. Focal length of a small concave mirror is 2.5 cm. In order to use this concave mirror as a dentist's mirror, what must be the distance of tooth from the mirror?
4. Ans. As a dentist's mirror needs a real and magnified image of the tooth, the tooth must be placed in between pole and focus. Therefore, the distance of the tooth must be less than focal length of 2.5 cm.
Q5. We wish to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm.
a. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror?
b. What is the nature of the image?
c. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
5. Ans. a. In order to obtain an erect image of an object with a concave mirror, the object should be at a distance less than its focal length. Therefore, here, the object must be placed at a distance less than 15 cm.
b. The nature of the image will be virtual. The image will be larger than the object
Q6. The image formed by a concave mirror is seen to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should we place the object?
6. Ans. We should place the object in between pole and focus of the mirror.
Q7. A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Where should an object be placed in front of this Concave mirror so as to obtain an image which is real, inverted and same size of the object?
7. Ans. When the object is placed at the centre of curvature, it produces an image, which is real, inverted and same size of the object. The distance of the centre of curvature from the pole is called radius of curvature and it is equal to twice of the focal length.
Hence, the object must be placed at a distance (2x20 = 40 cm) 40 cm from the pole in front of the concave mirror.
Q8. An object is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length 10 cm. Find the object distance if it produces a magnified real image?
8. Ans. If the object is placed in between focus and the centre of curvature, then the image produce is real and inverted and magnified. Therefore, the object must be in between focus (f) and centre of curvature (2f).
So, the object must be placed in between 10 cm to 20 cm from the pole in front of the mirror.
Q9. An object is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length 5 cm. Find the object distance if it produces a diminished real image?
9. Ans. When the object is beyond the centre of curvature of the concave mirror it produces a diminished real image. Therefore the object must be at least more than 2f = 2x5 cm = 10 cm from the pole in front of the mirror.
Q10. An object is 20 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright image or erect image. The radius of the curvature of the mirror is
a. Less than 20 mm b. Exactly 40 mm
c. In between 20 mm and 40 mm
d. More than 40 mm.
10. Ans. As for an erect image, object must be placed in between pole and focus, then focal length in this case is more than 20 mm. Therefore, the centre of curvature must be more than 2 x 20 mm = 40 mm.
d. is the correct answer.
Q11. Find the size, nature and position of image formed when an object of size 2 cm is placed at a distance of 9 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm.
11. Ans. Focal length, f = - 6 cm and object distance, u = - 9 cm. Height of the object, h₁ = 2 cm.
We know, mirror formula, 1/u + 1/v = 1/f
⟹ 1/v = 1/f - 1/u
⟹ 1/v = (u - f)/fu
⟹ v= fu/(u - f)
⟹ v = (-6)(-9)/( - 9 + 6) = (6x9)/(-3)
∴ v = - 18 cm (position)
Magnification,
m = (h₂/h₁) = (- v/u) = 18/(-9) = - 2
h₂ = m x h₁ = - 2 x 2 = - 4 cm (inverted)
Position: The image is 18 cm in front of the mirror.
Nature: The image is real, inverted and magnified.
Size: The image is 4 cm high, inverted and twice magnified and below the principal axis.
Q12. An object 1 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror which produces a real image 2 cm high. (i) what is the focal length of the mirror? (ii) find the position of the image.
Q13. A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 8 cm in front of it. Where is the image located? What is the focal length of the mirror?
Q14. What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror if the magnification produced by the mirror is (i) +2 (ii) - 0.50 ?
Q15. An object is placed at a distance 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
a. Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image.
b. Calculate the image distance.
c. State two characteristics of the image formed.
Q16. At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm should an object 1 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 4 cm tall?
Q17. When an object is placed at a distance of 4 cm from a concave mirror, its image is formed at 6 cm behind the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
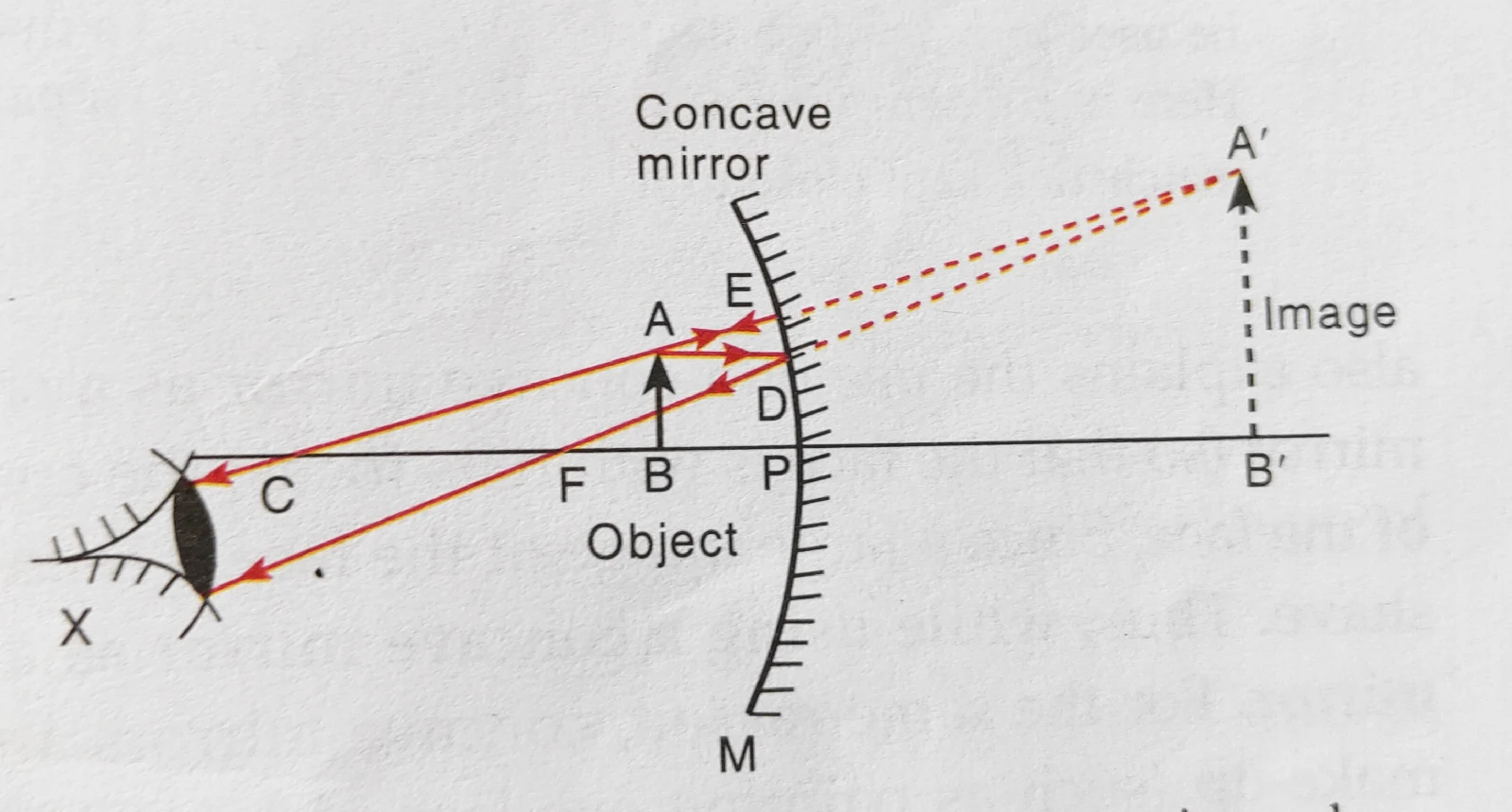
Q18. An object is placed in between principal focus and centre of curvature in front of a concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.



No comments:
Post a Comment