notes prepared by subhankar Karmakar
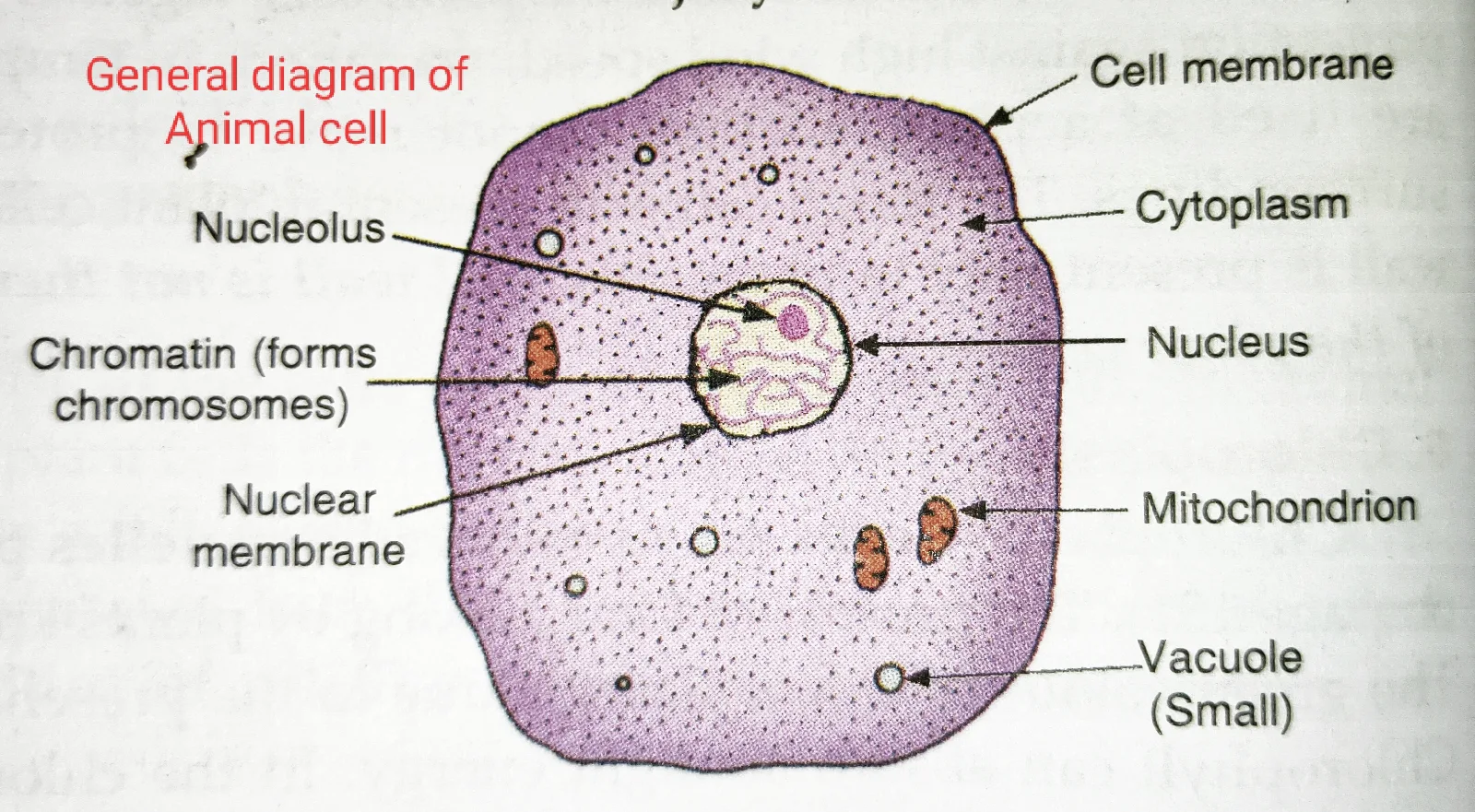
Comparison of Plant Cells and Animal Cells:
The main similarities between plant cells and animal cells are given below:
1. Plant cells and animal cells have a cell membrane or plasma membrane around them.
2. Plant cells and animal cells have cytoplasm.
3. Plant cells and animal cells have a nucleus.
4. Plant cells and animal cells have a nuclear membrane.
5. Plant cells and animal cells have mitochondria.
The main differences between plant cells and animal cells are given below:
1. A plant cell has a cell wall around it, but an animal cell does not have a cell wall around it.
2. A photosynthetic plant cell has chloroplasts in it. Other plant cells have different plastids in them, but in an animal cell there is no chloroplasts or other plastids.
3. A plant cell has a large vacuole in it, but an animal cell usually does not have any vacuole, some animal cells have small vacuoles.
Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells:
a. Prokaryotic cells and prokaryotes:
The primitive cells, where nucleus of the cell is not properly organised and they do not have any nuclear membrane around the nuclear material and they are called prokaryotic cells. In prokaryotic cells, the nuclear material is in direct contact with the cytoplasm.
The organisms made of prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes.
All the prokaryotes are simple, unicellular organisms. Most of the bacteria and blue green algae are prokaryotes.
b. Eukaryotic cells and Eukaryotes:
The cells having nuclear material enclosed by a nuclear membrane are called Eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a proper, well organised nucleus and nucleus are separated from the cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells are more advanced then prokaryotic cells.
The organisms which are made of Eukaryotic cells are called Eukaryotes. All the organisms other than bacteria and blue green algae are Eukaryotes. For example, Amoeba is an Eukaryote. Eukaryotes may be unicellular or multicellular.
Different organisms having variety in cell number, cell shape and cell size:
A. Variety in the number of cells:
Different organisms have different number of cells in their bodies.
B. Variety in shape of cells:
The cells in multicellular organisms have many different shapes.
C. Variety in size of cells:
The cells in multicellular organisms can have many different sizes.
A. Variety in the number of cells:
Depending on the number of the cells, in the body of an organism, an organism is called unicellular or multicellular.
(i) Unicellular Organisms:
The organisms which are made up of only one cell are called unicellular organism. It is also known as single celled organism. Some of the examples of unicellular organisms are:
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Chlamydomonas and bacteria.
The single cell of all the unicellular organisms behaves as a complete organisms. A unicellular organism can perform all the necessary life functions with the help of just one cell. For example, Amoeba is a tiny animal which consists of only one cell but can perform all the basic functions of life like taking food, digestion, respiration, movement, response to environmental changes, removal of waste and reproduction etc.
(ii) Multicellular Organisms:
The organisms which are made up of many cells are called multicellular organisms. Most of the plants and animals around us, including us are multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms millions and billions of cells which vary in shapes and sizes. Different groups of cells perform a variety of functions. A multicellular organism starts its life as a single cell called fertilized egg cell or Zygote.
B. Variety in shape of cells:
There are many types of cells in the bodies of multicellular organisms. These cells differ in shapes. For example, the shape of nerve cell in animals is very different from the shape of a muscle cell. A nerve cell is long and branched whereas a muscle cell is pointed at both ends and has a spindle shape and an epithelial cell is rectangular shape. Cells are different in shapes and sizes so that they can perform different functions. Some of the examples of animal cells which have different sizes and shapes are: nerve cell or neuron, muscle cell, epithelial cell, red blood cell, white blood cells, bone cell and cartilage cell.
Different shape of a cell helps in its functioning. Like nerve cells are long and have projections so that they can make contacts with many other Nerve cells and carry messages over long distances like between brain and other parts of body. Muscle cells bring about the moment at body parts by contracting and relaxing, hence, they are pointed at the both ends and spindle shaped.
Some of the important plant cells are: epidermal cells, xylem cells, phloem cells, and photosynthetic cells. The epidermal cells form a layer around the plant organs and protect the cells below from injury, xylem cells are the tube like plant cells having thick and strong walls which carry water and mineral salts from the roots of the plant to the leaves. Phloem cells are also tubelight plant cells having thin walls which carry the food made by leaves to all other parts of the plant. The photosynthetic cells of the plant contain chlorophyll and prepare food by photosynthesis. The mesophyll cells of leaf are the photosynthetic plant cells. These cells in the leaf of a plant are specially adapted for making food by photosynthesis.
Amoeba:
All the plant and animal cells are not capable of independent existence, the single celled organism like amoeba can exist independently.
The shape of amoeba cell is irregular. In fact the Amoeba cell has no fixed shape. The
Amoeba cell keeps on changing its shape continuously. Shape of Amoeba cell changes because amoeba can make its cytoplasm in any direction it wants to. The Amoeba cell finger like projections of varying lengths protruding out of his body which is called pseudopodia.
Amoeba derives two advantages by changing shape:
The changing of shape due to the formation of pseudopodia helps amoeba in
1. movement
2. In capturing food.
C. Variety in size of cells:
The cells are of many different sizes. Some are so small that they cannot be seen with the naked eyes, whereas large cells also exists. Generally most of the cells are extremely small in size, like bacteria cells have a length of 0.1 micrometer ~ 0.5 micrometer. The smallest cell is bacteria mycoplasma, which is only 0.1 micrometre long. Whereas, the birds eggs are very large cells, they can be seen easily with naked eye. Each egg of the bird is a single cell, like the hen's egg is a single cell. The biggest cell is the ostrich egg which is approximately 17 cm long. The size of cells has no relation with the size of the body of an animal. Rather it is related to its function.




1 comment:
Thank you Sir for such helpful notes.......
Post a Comment