Monday, 29 November 2021
LECTURE - 1 : CLASS VIII : SCIENCE : CHAPTER 13 : SOUND
Friday, 26 November 2021
LECTURE - 3 : CLASS VIII : SCIENCE : CHAPTER 12 : FRICTION
Sunday, 19 September 2021
MCQ -1: CLASS XII: PHYSICS ELECTROSTATIC CHARGE AND FIELDS
Thursday, 16 September 2021
LECTURE - 2 : CLASS VIII : SCIENCE : CHAPTER 10 : REACHING THE AGE OF ADOLESCENCE
LECTURE - 1 : CLASS VIII : SCIENCE : CHAPTER 11 : FORCE AND PRESSURE
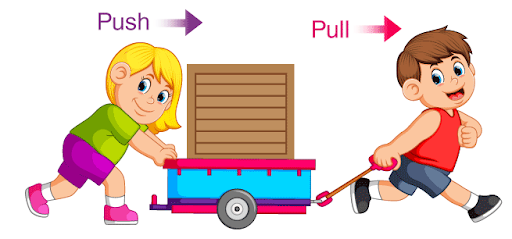
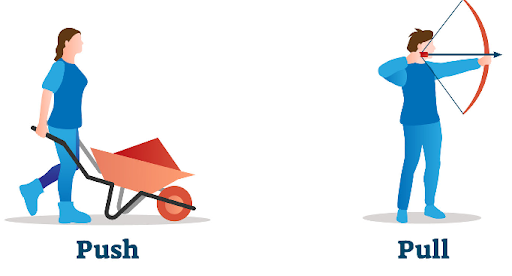
FORCE
· A push or pull on an object is called force.
·
Forces are used in our everyday
actions like pushing, pulling, lifting, stretching, twisting and pressing.
Force is due to an interaction:
·
When two
objects interact with each other, they can exert forces on each other. These
forces can either attract or repel the objects, depending on the nature of the
interaction.
Force has magnitude as well as direction:
·
The strength of a force is expressed
by its magnitude.
·
The magnitude of force is expressed
in the the SI unit of force called Newton. Its symbol is N.
·
1 Newton is the force which can make
an object of 1 kg mass to move an acceleration of 1 m/s².
·
When two forces act along the same
direction, then the net force acting on the object is equal to the sum of the
two forces and when they act in opposite direction, and then the net force
acting on the object is equal to the difference between the two forces.
·
If the two forces applied to an
object are equal in magnitude and act in opposite directions, then the net
force acting on the object is zero.
EFFECTS OF FORCE:
A force can produce the following
effects.
·
A force can move a stationary
object.
·
A force can stop a moving object.
·
A force can change the speed of a
moving object.
·
A force can change the direction of
a moving object.
·
A force can change the shape and
size of an object.
TYPES OF FORCES
The most common types forces are:
·
Muscular
force
·
Frictional
force
·
Magnetic
force
·
Electrostatic
force and
·
Gravitational
force.
CONTACT FORCES
A force which can be exerted bi an
object on another object only through physical touching or contact is called a
contact force. Examples of contact forces are
·
Muscular
force and
·
Frictional
force
MUSCULAR FORCE
The force exerted by the muscles of
the body is called muscular force.
As the muscular force can be applied
to an object only when our body or body of an animal is in contact with the
object, therefore, muscular force is a contact force.
FRICTIONAL FORCE OR FRICTION
The force which always opposes the
motion of one body over another body is called frictional force or
friction.
Since frictional force arises only when the surfaces of two objects are in touch with each other, frictional force is an example of of contact force.
NON CONTACT FORCES
A force which can be exerted bi an
object on another object even from a distance without touching each other is
called a non contact force.
The examples of non contact forces
are
·
Magnetic
force
·
Electrostatic
force and
·
Gravitational
force.
MAGNETIC FORCE
The force exerted by a magnet is called magnetic force.
Since a magnet can exert its
magnetic force on iron objects from a distance even without touching them,
therefore, magnetic force is a non contact force. The magnetic force between a
magnet and an iron object is always that of attraction. A magnet can attract or
repel another magnet.
A magnet has two poles, North Pole
and South Pole.
There is a magnetic force of
repulsion between the like poles of two magnets and there is a magnetic force
of attraction between the unlike poles of two magnets.
The magnetic force is widely used in
our everyday life.
ELECTROSTATIC FORCE
There are two types of electric
charges. They are Positive electric charges and Negative electric
charges.
The force exerted by an electrically
charged object is called electrostatic force. As an example, when a plastic
comb is rubbed in dry hair, it gets electric charges and this electrically
charged comb can attract tiny pieces of paper.
Electrostatic forces may be
attractive or repulsive. Electrostatic force between two like charges is
repulsive and between two unlike charges is attractive. Therefore we can say, a
positive charge repel another positive charge but attracts a negative
charge.
The electrostatic force can be
exerted by a charged object on another object from a distance even when they
are not in touch with each other; therefore, electrostatic force is an example
of non contact forces.
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
The pull exerted by objects possessing
mass on another mass is called gravitational forces. Gravitational force
between two objects is a force of attraction.
It is the gravitational force
between the sun and the earth which holds the earth in its orbit around the
sun.
The force with which the earth is
the objects towards it, is called the force of gravity or simply gravity.
The force of gravity causes all the
objects to fall towards the earth.
The gravitational force of Earth or
gravity acts on objects from a distance without there being a physical contact,
therefore, gravitational force or gravity is an example of non contact
forces.
PRESSURE
Pressure is produced when a force
acts on an object. The force acting on an object per unit surface area of the
object is called pressure.
The effect of a force depends on the
area of the object on which it acts.
Pressure = Force / Area
The SI unit of pressure is Newton
per square metre ( N/m²), which is also called Pascal
(Pa).
1 Pa = 1 N/m²
1 kilo Pascal (1 kPa = 1000
Pa) is equal to 1000 Pascal.
FACTORS ON WHICH PRESSURE DEPENDS
The pressure depends on two factors.
·
The force
applied
·
Area over
which force acts.
The same force can produce different
pressures depending on the area over which it acts. For example, when a force
acts over a large area of an object, it produces small pressure. But if the
same force acts over a small area of the object, it produces a large
pressure.
WHY SCHOOL BAGS HAVE WIDE STRAPS
A school bag or a shoulder bag has
wide strap made of thick cloth so that the weight of bag may fall over a large
area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure on the shoulder. And
due to less pressure it is more comfortable to carry the heavy school
bag.
WHY A SHARP KNIFE CUTS BETTER THAN A BLUNT KNIFE
A sharp knife has a very thin edge
to its blade. A sharp knife cuts objects like vegetables better because due to
its very thin edge, the force of our hand falls over a very small area of the
object producing a large pressure. And this large pressure cuts the object
easily. On the other hand, a blunt knife has a thicker edge. A blunt knife does
not cut an object easily because due to its thicker edge, the force of our
hands falls over a larger area of the object and produces lesser pressure. This
lesser pressure cuts the object with difficulty.
WHY THE TIP OF A NEEDLE IS SHARP
The tip of a sewing needle is sharp
so that due to its sharp tip, the needle may put the force on a very small area
of the cloth producing a large pressure sufficient to Pierce the cloth being
stitched. A knife Razer blade and an x are the cutting tools where is a sewing
needle is a piercing tool.
WHY THE DEPRESSION IS MUCH MORE WHEN A MAN STANDS ON THE CUSHION THEN
WHEN HE LIES DOWN ON IT
When a man stands on a cushion then
only his two feet having small area are in contact with the cushion. Due to
this the weight of man falls on a small area of the cushion producing a large
pressure. This large pressure causes a big depression in the cushion. On the
other hand, when the same man is lying on the cushion then his whole body
having larger area is in contact with the cushion producing much smaller
pressure. This smaller pressure produces a very little depression in the
cushion.
PRESSURE EXERTED BY LIQUIDS
All the liquids exert pressure on
the base and the walls of their containers. All the liquids have weight and
this weight acts on the base of the vessel producing a pressure.
The pressure of a liquid increases
with depth. The greater the depth of a point in a liquid the greater is the
pressure. Liquids also exert pressure on the walls of the vessel in which they
are stored. The sideways pressure exerted by liquids also increases with the
depth of the liquid.
The formation of mountains of water
from the leaking pipes of water supply pipeline tells us that water exerts
pressure on the walls of the container.
A liquid exerts pressure in all
directions even upwards.
PRESSURE EXERTED BY GASES
All the gases exert pressure on the
walls of their containers. Air pressure arises due to the constant solutions of
the tiny molecules of the gases present in air with the walls of the container
or vessel in which it is enclosed.
High air pressure produces by the
gas molecules on the walls of balloon causes it to extend and get
inflated.
Two examples that gases like air
exert pressure are:
·
When air is filled into a balloon
with our mouth the balloon gets inflated.
·
When air is filled into a bicycle tube
with a pump the tube gets integrated and makes the tyre feel hard.
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
The layer of air above the earth is called atmosphere. Air has weight show the atmosphere consisting of tremendous amount of air has enormous weight the weight of atmosphere exerts a pressure on the surface of the earth and on all the objects on the Earth including ourselves. This pressure is known as atmospheric pressure. The atmospheric pressure is due to the weight of air present in the atmosphere above us. Atmospheric pressure also acts in all directions.
MAGNITUDE OF ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
Atmospheric pressure is equal to the weight of air present in a BD tall column of air standing on one square metre area of the earth. As we go up in the atmosphere from
the surface of Earth the atmospheric pressure goes on decreasing. On the
surface of Earth, the atmospheric pressure is maximum at the sea level. The
atmospheric pressure on the top of a high mountain will be much less than at
its base.
Although pressure is is measured in
Pascal, atmospheric pressure is measured in mm of Mercury. The atmospheric
pressure on the surface of earth at the sea level is 760 mm of Mercury.
OUR BODY AND ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
Change the atmospheric pressure acting on our body from outside is balanced by the blood pressure acting from inside we do not get crushed. But there is an effect of low atmospheric pressure in our body. At higher altitudes, atmospheric pressure becomes much less than our blood pressure. Since our blood is at a higher pressure than outside pressure, therefore, some of the blood vessels in our body burst and nose bleeding takes place at high altitudes.
APPLICATIONS OF ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1. DRINKING STRAW
 The drinking straw works on the
existence of atmospheric pressure. The lower end of drinking straw is dipped in
the soft drinks. When we suck at the upper end of the straw with our mouth, the
pressure of air inside the straw and in our mouth is reduced. The pressure
acting on the surface of the soft drink is equal to atmospheric pressure. So,
the greater atmospheric pressure acting on the surface of the soft drink pushes
the soft drink up the straw into our mouth.
The drinking straw works on the
existence of atmospheric pressure. The lower end of drinking straw is dipped in
the soft drinks. When we suck at the upper end of the straw with our mouth, the
pressure of air inside the straw and in our mouth is reduced. The pressure
acting on the surface of the soft drink is equal to atmospheric pressure. So,
the greater atmospheric pressure acting on the surface of the soft drink pushes
the soft drink up the straw into our mouth. 2. SYRINGE
 A glass tube or plastic tube with a
nozzle and piston for sucking in and ejecting liquid in a thin stream is called
a syringe. The series works on the existence of atmospheric pressure. When the
nozzle of a syringe is dipped in a liquid and its piston is withdrawn, the
pressure inside the syringe is lowered. The greater atmospheric pressure acting
on the surface of the liquid pushes the liquid up into the syringe.
A glass tube or plastic tube with a
nozzle and piston for sucking in and ejecting liquid in a thin stream is called
a syringe. The series works on the existence of atmospheric pressure. When the
nozzle of a syringe is dipped in a liquid and its piston is withdrawn, the
pressure inside the syringe is lowered. The greater atmospheric pressure acting
on the surface of the liquid pushes the liquid up into the syringe.
3. DROPPER
 The dropper is a small glass tube
with a rubber ball at one end and a nozzle at the other. Its functionality
relies on atmospheric pressure. To use the dropper, we immerse the nozzle in
the liquid and squeeze the rubber ball, causing air inside the tube and bulb to
escape as bubbles. This action lowers the air pressure within the dropper. Once
we release the rubber bulb, the higher atmospheric pressure outside the dropper
forces the liquid to be drawn up into the tube.
The dropper is a small glass tube
with a rubber ball at one end and a nozzle at the other. Its functionality
relies on atmospheric pressure. To use the dropper, we immerse the nozzle in
the liquid and squeeze the rubber ball, causing air inside the tube and bulb to
escape as bubbles. This action lowers the air pressure within the dropper. Once
we release the rubber bulb, the higher atmospheric pressure outside the dropper
forces the liquid to be drawn up into the tube.4. RUBBER SUCKER
 A rubber sucker, also known as a
suction cup, is a rubber device that adheres firmly to flat and smooth surfaces
when pressed. Its appearance resembles a small concave rubber cup. When we
apply the rubber sucker to a flat, smooth surface and press it, the concave
rubber cup flattens significantly, expelling most of the air from underneath.
This compression results in a significant reduction in air pressure inside the
rubber sucker. As a consequence, the higher atmospheric pressure from the
outside effectively secures the rubber sucker in place on the flat surface.
A rubber sucker, also known as a
suction cup, is a rubber device that adheres firmly to flat and smooth surfaces
when pressed. Its appearance resembles a small concave rubber cup. When we
apply the rubber sucker to a flat, smooth surface and press it, the concave
rubber cup flattens significantly, expelling most of the air from underneath.
This compression results in a significant reduction in air pressure inside the
rubber sucker. As a consequence, the higher atmospheric pressure from the
outside effectively secures the rubber sucker in place on the flat surface.