RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
Respiration in plants involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and they are called respiratory gases.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN RESPIRATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
|
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS |
RESPIRATION IN ANIMALS |
|
· All the parts of a plant (like root, stem and leaves) perform respiration individually |
In animals, respiration is performed as a single unit. |
|
· Transport of respiratory gases from one part to another is limited. |
Respiratory gases are usually transported over long distances inside an animal. |
|
· Respiration in plants occurs at a slow rate. |
Respiration in animals occurs at a faster rate |
· Plants have a large surface area in comparison to its volume. Therefore, in plants, oxygen is supplied to all the cells of the body with the help of diffusion only.
· Diffusion in plants occurs in the roots, stems and leaves.
1. RESPIRATION IN ROOTS
· The extensions of epidermal cells of a root are called root hair. The root hairs are in contact with the air of the soil. Oxygen from air diffuses into root hair and reaches all the cells of the root for respiration.
· Carbon dioxide produced in the cells of the root during respiration moves out through the same root hairs by the process of diffusion.
· Land plants die if their roots remain waterlogged for a longer period of time as water displaces the air in the soil and roots are forced to respire through anaerobic respiration and thus produce ethanol. This may kill the plant.
2. RESPIRATION IN STEMS
· Soft stems of small herbaceous plants have stomata. Oxygen from air diffuses into the stem through stomata and carbon dioxide produced during respiration moves out from the stem through the same stomata.
· The hard and woody stems of large tree do not have stomata. In woody stems, bark has lenticels for gaseous exchange. Lenticels is a small area of bark in a woody stem where the cells are loosely packed allowing the gaseous exchange to take place between the air and the living cells of the stem.
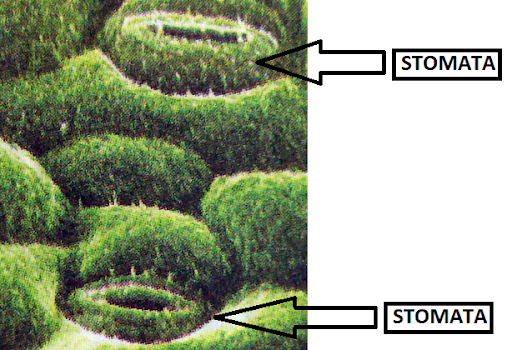
3. RESPIRATION IN LEAVES
· The leaves of a plant have tiny pores called stomata. The exchange of respiratory gases in the leaves takes place by diffusion through stomata.
· Respiration in the leaves occurs during the day time as well as at night. Photosynthesis occurs only during the day time.
· The net gaseous exchange in the leaves of a plant is as follows:
· During day time, when photosynthesis occurs, oxygen is produced. The leaves use some of the oxygen for respiration and rest of the oxygen is diffused into the air. The carbon dioxide produced during respiration is all used up in the photosynthesis by leaves. Hence, the net gas exchange in leaves during day time is: O2 diffuses out and CO2 diffuses in.
· At night oxygen from the air diffuses into the leaves to carry out respiration and the carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses out. Hence, the net gas exchange in leaves during day time is: O₂ diffuses in and CO₂ diffuses out.





No comments:
Post a Comment